Array Node
Overview
The Array Node is used to construct an array from one or more inputs of any type. It can also be used to merge multiple arrays into a single array using the Flatten setting.
By default, inputs will be flattened, so if any of the inputs are arrays themselves, they will be merged into the output array. This behavior can be disabled by unchecking the Flatten setting.
- Inputs
- Outputs
- Editor Settings
Inputs
| Title | Data Type | Description | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input [i] | any | The ith input to be added to the array | N/A | Dynamic number of inputs based on how many connections there are |
Outputs
| Title | Data Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Output | any[] | The array created from the inputs | The output will be a single array containing all valid inputs |
| Indices | number[] | The indices of the elements in the array | The output will be an array of numbers representing the array indices |
Editor Settings
| Setting | Description | Default Value | Use Input Toggle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flatten | If enabled, array inputs will be flattened before joining | true | No |
| Deep | If enabled, array inputs will be flattened recursively | false | No |
Example 1: Creating an Array from Multiple Inputs
Let's say you have three Text nodes: one with the value "Hello", another with the value "World", and the last one with the value "!". If you want to create an array from these three strings, you can do the following:
- Add an Array Node to your graph.
- Connect the output of the first Text node to
Input 1of the Array Node. - Connect the output of the second Text node to
Input 2of the Array Node. - Connect the output of the third Text node to
Input 3of the Array Node.
The Output of the Array Node will now be ["Hello", "World", "!"].
Example 2: Creating an Array from Array Inputs
Imagine you have two Array nodes: one with the value ["One", "Two"] and the other with the value ["Three", "Four"]. If you want to create a new array from these two arrays, you can do the following:
- Add an Array Node to your graph.
- Connect the output of the first Array node to
Input 1of the Array Node. - Connect the output of the second Array node to
Input 2of the Array Node. - Enable the
Flattensetting.
The Output of the Array Node will now be ["One", "Two", "Three", "Four"].
Example 3: Creating an Array without Flattening
If you want to create an array from arrays without flattening them, you can do the same steps as in Example 2, but leave the Flatten setting disabled. The Output of the Array Node will then be [["One", "Two"], ["Three", "Four"]].
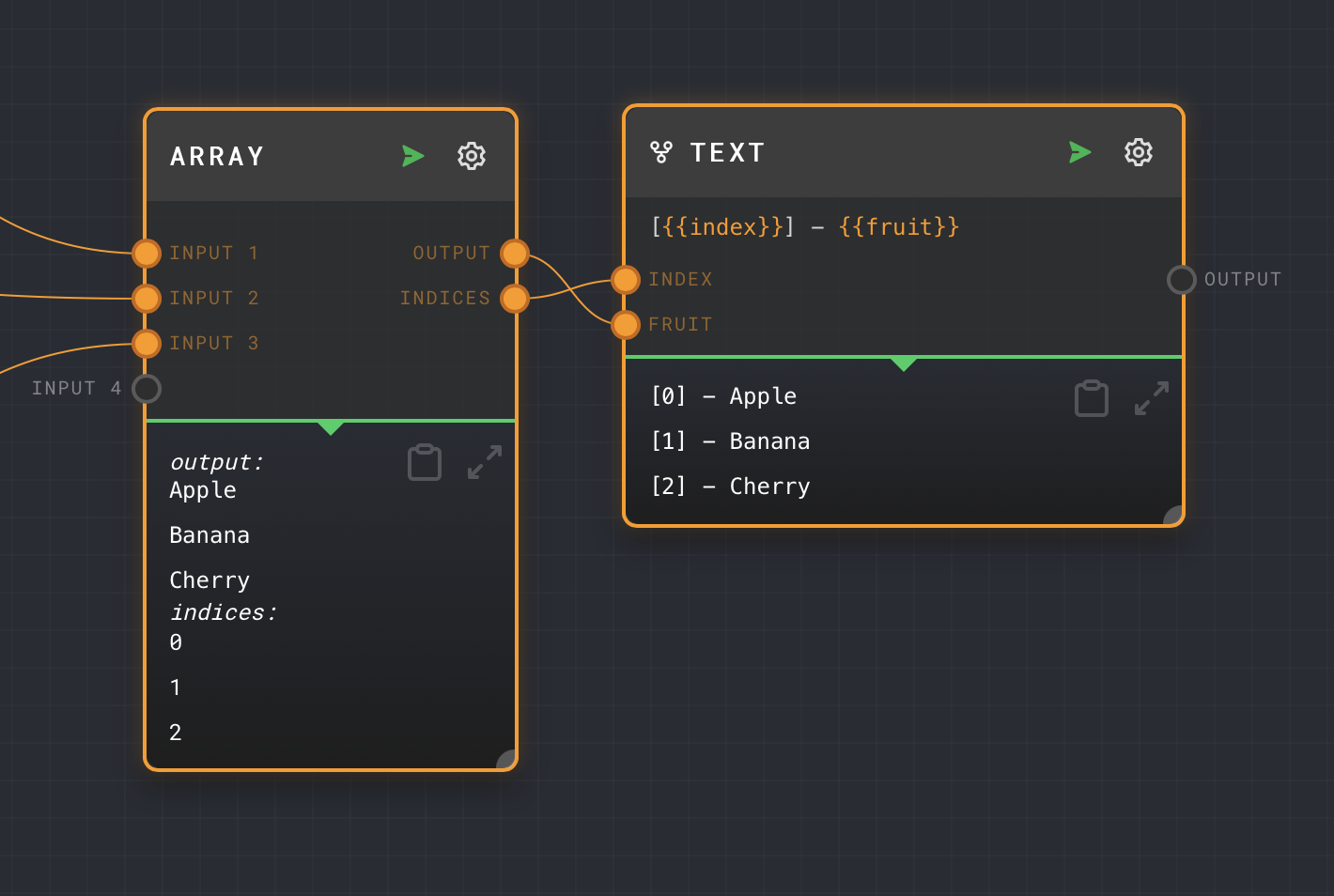
Example 4: Using the Indices Output
Let's say you have an Array Node with the value ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"]. If you want to create a new array where each element is a string that includes the index and the corresponding fruit name from the original array, you can do the following:
- Add a Text Node to your graph with the text
"[{{index}}] - {{fruit}}". - Connect the
Outputof the Array Node to theFruitinput of the Text Node. - Connect the
Indicesoutput of the Array Node to theIndexinput of the Text Node. - Enable the
Splitsetting on the Text Node.
The Output of the Text Node will now be ["[0] - Apple", "[1] - Banana", "[2] - Cherry"].
In this example, the Indices output of the Array Node gives us an array of indices that corresponds to the elements of the original array. We then use these indices along with the original array elements to create a new array of formatted strings. The Split setting ensures that the Text Node generates a separate output for each element of the input arrays.
Flattening Arrays
The Array Node has a Flatten setting. When enabled, this setting treats each element of an array input as a separate element to be added to the main array. This is particularly useful when you're dealing with array inputs and want to merge all elements of these arrays into a single array.
Note that with flatten disabled you can get arrays of arrays. These are not well supported in Rivet and you may have to use a Code Node to work with them.
If the Deep setting is enabled, the Array Node will recursively flatten all array inputs. This means that if an array input contains another array, the Array Node will flatten the inner array as well. You can
use the Array Node as a Flatten node this way.
Error Handling
If an input is missing or null, the Array Node will simply ignore it during the array creation process. This can be useful when dealing with optional inputs that may not always be present.
Q: What happens if I connect a non-array node to the Array Node?
A: The Array Node is designed to work with any type of inputs. If a non-array input is connected, the node will treat it as a single element to be added to the array.
Q: Can I connect an Array Node to another Array Node?
A: Yes, you can connect an Array Node to another Array Node. If the Flatten setting is enabled, each element of the input array will be treated as a separate element to be added to the main array. If Flatten is disabled, the input array will be added as a single element to the main array.
Q: What happens if an input is missing or null?
A: If an input is missing or null, the Array Node will simply ignore it during the array creation process. This can be useful when dealing with optional inputs that may not always be present.