Compare Node
Overview
The Compare Node allows you to perform a comparison operation between two input values. The node supports a variety of comparison functions including equality, inequality, less than, greater than, and logical operations such as AND, OR, XOR, NAND, NOR, and XNOR.
- Inputs
- Outputs
- Editor Settings
Inputs
| Title | Data Type | Description | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | any | The first value for comparison. | (Required) | None |
| B | any | The second value for comparison. | (Required) | None |
Outputs
| Title | Data Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Output | boolean | The result of the comparison operation. |
Editor Settings
| Setting | Description | Default Value | Use Input Toggle | Input Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison Function | The comparison function to be used for the operation. Available options are '==', '<', '>', '<=', '>=', '!=', 'and', 'or', 'xor'. | '==' | Yes | string |
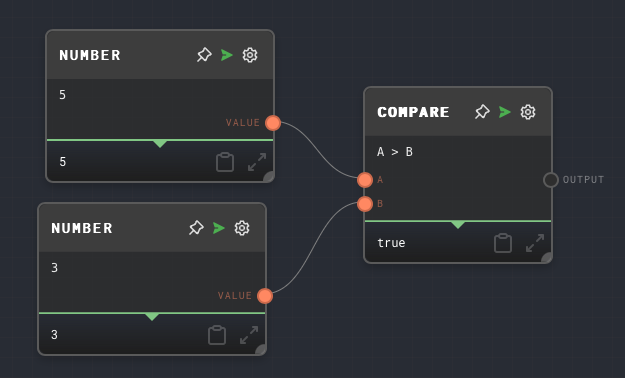
Example 1: Compare two numbers
- Create a Compare Node and set the
Comparison Functionto>. - Create two Number Nodes, one with the value
5and the other with the value3. - Connect the Number Nodes to the
AandBinputs of the Compare Node respectively. - Run the graph. Note that the output of the Compare Node is
true, because 5 is greater than 3.
Error Handling
The Compare Node does not have any specific error handling. If the inputs are not of the same type, the node will attempt to coerce the second input (B) to the type of the first input (A).
FAQ
Q: What happens if the inputs are not of the same type?
A: If the inputs are not of the same type, the node will attempt to coerce the second input (B) to the type of the first input (A). If the coercion is not possible, the comparison will be performed with the original values.
Q: Can I use the Compare Node to compare arrays or objects?
A: Yes, you can use the Compare Node to compare arrays or objects. However, the comparison will be performed using JavaScript's strict equality (===), which may not give the expected results for arrays or objects. For a deep comparison of arrays or objects, consider using a Code Node.